Baking technique is more than just a cooking method; it’s a centuries-old culinary art that is both versatile and transformational. From golden loaves of bread to delicate pastries, the process of baking turns raw ingredients into edible masterpieces. As part of the dry heat cooking family, baking technique uses persistent heat and precision to deliver everything from classic desserts to hearty meals. Whether you’re a baking enthusiast or a chef-in-the-making, understanding its principles is essential for refining your culinary skills.
This guide dives deep into what makes baking technique unique, how it relates to science, and provides key techniques, expert tips, and recipes to help you master this dry heat method.
What is Baking technique?
Baking technique is a dry heat cooking method where food is surrounded by and cooked through consistent heat, typically in an oven. Unlike roasting, which often involves larger cuts of meat or vegetables, baking is usually associated with pastries, bread, and desserts. This method relies on precision, as the right balance of temperature, timing, and ingredients can drastically affect the final result.
Why is baking so significant? Because it’s a universal technique that transcends cultures and cuisines. From French croissants to Italian pizzas, Indian naans to American cookies, baking weaves a global culinary thread.
Objective for today? To learn the science, secrets, and skills needed to perfect baked goods in your kitchen.
The Principles of Baking technique
How Dry Heat Works in Baking technique
The magic of baking stems from the dry heat in an oven. Unlike boiling or steaming, which use water as the primary medium, dry heat evaporates moisture and creates a crisp crust, giving baked goods distinct textures.
- Crust Formation: Dry heat caramelizes sugars and proteins on the surface of food, creating a golden, crisp crust.
- Internal Cooking: Heat penetrates the food, causing chemical reactions that rise batters or transform soft dough into firm products.
The Science Behind Baking technique
Baking technique is as much about science as it is about creativity. Key chemical reactions include:
- Maillard Reaction: A browning reaction between sugars and amino acids that creates a golden crust.
- Cooling and Setting: During cooling, the gluten and starch gel set into a solid structure.
Precision Matters
Temperature, measurements, and timings are non-negotiable in baking. A slight change in any of these can affect texture, rise, or flavor.
Types of Baking techniques
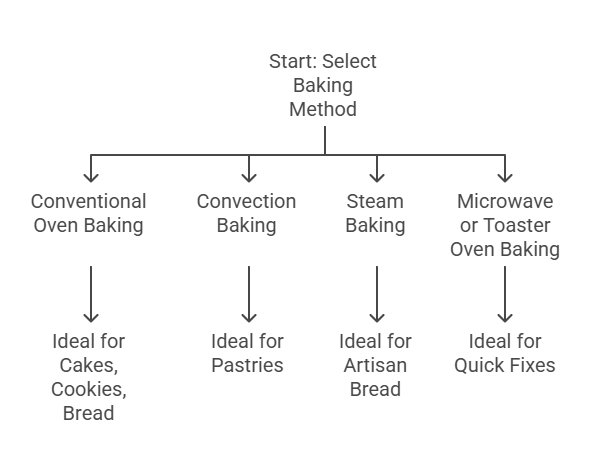
1. Conventional Oven Baking
This traditional technique uses consistent, radiant heat. Ideal for cakes, cookies, and bread, it’s the most common baking approach.
Example Recipe: Chocolate chip cookies.
2. Convection Baking
Convection ovens have fans that circulate hot air, ensuring even cooking. Perfect for pastries like croissants or biscuits where even browning is key.
Tip: Lower temperatures by 10-20°F when using convection settings.
3. Steam Baking
Adding steam during baking enhances moisture and creates shiny, crusty surfaces—ideal for artisan bread.
Example Recipe: Rustic sourdough bread.
4. Microwave or Toaster Oven Baking
Great for small spaces or quick fixes like mug cakes. These methods are less precise but offer convenience.
Example Recipe: 3-minute chocolate mug cake.
When selecting a method, consider the recipe’s specific requirements—texture, crust, and bake time.
Common Ingredients Used in Baking technique
Key Ingredients
- Flour forms the structure. Choose all-purpose, whole wheat, or gluten-free depending on needs.
- Sugar sweetens and aids in browning. Options include granulated, brown, and coconut sugar.
- Fats (e.g., butter, oil) provide richness and tenderness.
- Eggs offer moisture, structure, and act as a binder.
The Role of Leavening Agents
Leaveners like baking powder, soda, or yeast make dough rise by producing air pockets.
Tip: Baking soda requires acid (e.g., vinegar), while baking powder already contains acid.
Gluten-Free and Vegan Alternatives
For inclusivity, try almond flour, aquafaba (as an egg substitute), or coconut oil.
Must-Have Baking Tools
A baker’s success starts with well-chosen tools:
Essentials
- Measuring cups and spoons for precise measurements.
- Mixing bowls in various sizes.
- Baking trays and pans for uniform results.
Advanced Tools
- Pastry cutter for pie dough.
- Piping bags for decoration.
Maintenance Tip: Keep tools clean and store them properly to ensure longevity.
Tips for Successful Baking
- Preheat Your Oven
This ensures even baking right from the start. Never skip this step!
- Measure Exactly
Baking is an exact science, so use proper tools for dry and liquid ingredients.
- Understand Baking Terminology
- Cream: Mix butter and sugar until fluffy.
- Fold: Gently combine without deflating air.
- Sift: Remove clumps for even texture.
- Avoid Common Mistakes
- Don’t open the oven too early; it can cause cakes to sink.
- Use room-temperature ingredients unless otherwise specified.
- Experiment Wisely
Practice leads to perfection, so don’t hesitate to try new recipes and techniques.

The Joy of Baking at Home
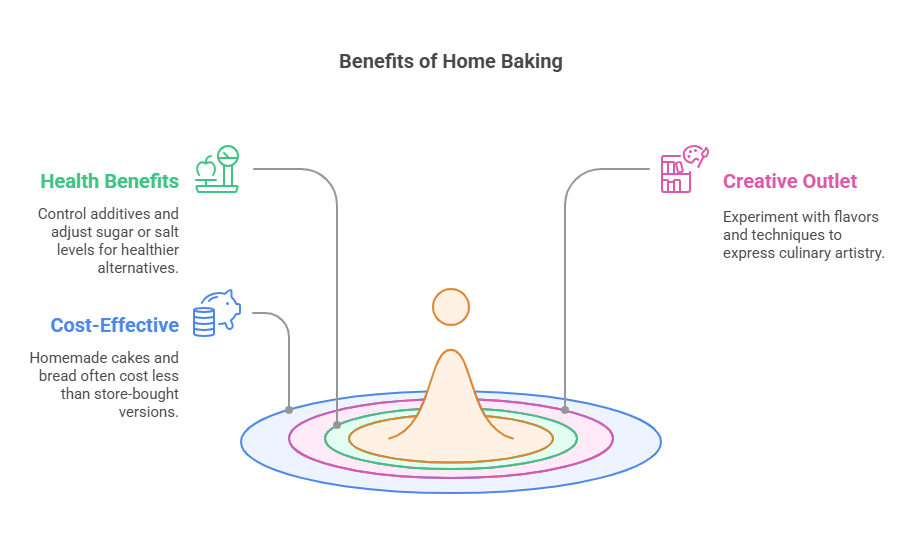
- Health Benefits
Control additives and adjust sugar or salt levels for healthier alternatives.
- Creative Outlet
Experiment with flavors and techniques to express culinary artistry.
- Cost-Effective
Homemade cakes and bread often cost less than store-bought versions.
Baking isn’t just about food; it’s about creating experiences, memories, and joyful moments to share with loved ones.
Simple Recipes to Begin Baking
Beginner Recipes
- Banana Bread: Moist and foolproof!
- Classic Chocolate Chip Cookies: Perfect for any occasion.
Intermediate Recipes
- Sourdough Bread: Master the art of fermentation.
- Layered Cake: Great for celebrations.
Family Favorites
- Apple Pie: A warm and comforting dessert.
Start with accessible recipes and gradually build your expertise!
Frequently Asked Questions About Baking technique
- Why does my cake sink in the middle?
This often happens when the batter is undercooked or the oven door is opened too early.
- How do I know when bread is done?
Tap the bottom of the loaf—it should sound hollow.
- What’s the difference between baking powder and soda?
Baking soda needs acid to activate, while baking powder includes acid.
Final Thoughts
Baking technique is an essential part of the dry heat cooking method, blending art and science into something magical. With the tips, techniques, and recipes shared here, you now have the tools to take your baking skills to the next level.
Don’t stop here—explore the rest of our blog for more techniques, including roasting, grilling, and broiling. Happy baking!
📌 Stay connected with us!
- Follow us on Instagram: @RoastedKitchen25 for daily baking inspiration.
- Tag us in your creations using #RoastedKitchenBakes—we’d love to see what you make!
- Subscribe to our newsletter for exclusive recipes, expert tips, and kitchen hacks straight to your inbox!

Hi, I’m Mayaz Ahsan!
As a passionate cook, storyteller, and food enthusiast, I combine my love for travel, farming, reading, and teaching to bring you insightful culinary tips and stories. Welcome to Roasted Kitchen – I’m thrilled to share this journey with you!










 Subscribe to our free newsletter for tips, tutorials, and insights!
Subscribe to our free newsletter for tips, tutorials, and insights!